Your journey to motherhood is significantly influenced by how you nourish your body. A healthy diet creates a strong foundation for conception and a healthy pregnancy, preparing your body for the changes ahead.
Understanding the powerful connection between nutrition and reproductive health is key to taking charge of your fertility journey.
Dietary choices play a significant role in your ability to conceive, and improving egg quality is crucial for enhancing fertility and sustaining a healthy pregnancy.
Recent research suggests that diet and lifestyle changes can improve fertility outcomes by nearly 70 percent in women with ovulatory disorders. This shows how powerful nutrition can be in shaping reproductive health.
Understanding Female Fertility and Nutrition:
A balanced, nutrient-rich diet supports female reproductive health in several ways. It ensures the body receives essential nutrients like folic acid, which is vital for healthy egg development, preventing birth defects, and reducing the risks of ovulatory infertility.
Maintaining an optimal weight is also crucial, as being either underweight or overweight can lead to hormonal imbalances that hinder conception.
Nutrition also influences hormone regulation, blood circulation, and stress levels. For women with PCOS, a fertility-focused diet helps manage insulin resistance and promotes more regular cycles.
The quality of eggs is equally important. While women cannot increase the number of eggs, diet and lifestyle choices can significantly improve their quality, leading to higher chances of conception.
Also Read: How Many Injections Are Needed for IVF Treatment?
Best Foods to Increase Fertility in Females:
The best way to boost fertility naturally is by including a variety of nutrient-rich foods in your daily meals.
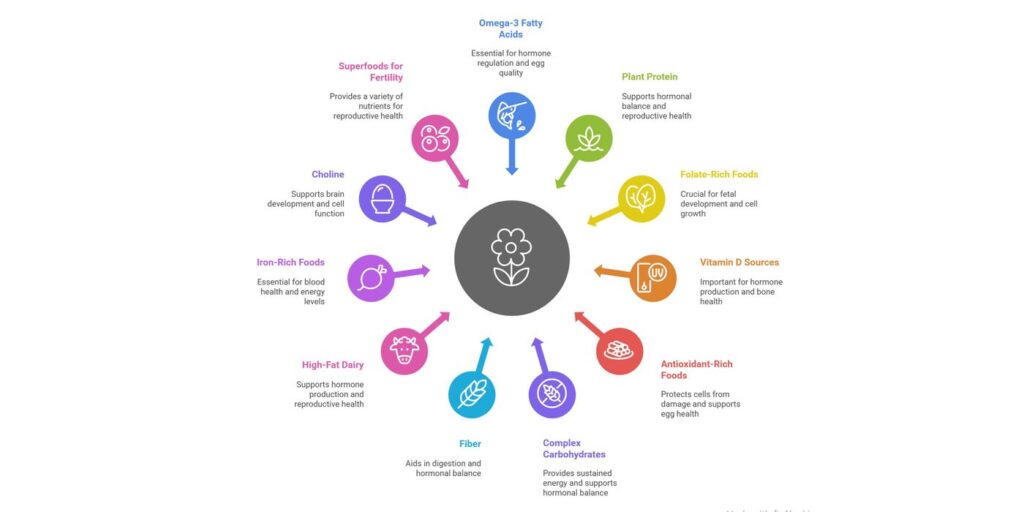
1. Omega-3 fatty acids:
Omega-3s improve blood flow to reproductive organs, regulate hormones, enhance egg quality, and delay egg aging. Great sources are oily fish such as salmon and sardines, flaxseed, chia seeds, walnuts, and enriched eggs.
2. Plant protein:
Higher intake of plant-based protein is linked to reduced risk of ovulatory infertility. Good options include lentils, chickpeas, quinoa, and nuts. While animal protein can be consumed in moderation, excessive intake may negatively impact fertility.
3. Folate-rich foods:
Folate supports healthy egg development and reduces neural tube defects in early pregnancy. Include spinach, kale, asparagus, legumes, citrus fruits, and fortified cereals.
4. Vitamin D sources:
Vitamin D helps regulate hormones and supports ovulation. It is found in salmon, egg yolks, fortified milk, and UV-treated mushrooms.
5. Antioxidant-rich foods:
Antioxidants fight oxidative stress and protect reproductive cells. Add berries, citrus fruits, spinach, nuts, and turmeric to your diet.
6. Complex Carbohydrates:
Whole grains like oats, brown rice, and quinoa maintain stable insulin levels and support hormonal balance.
7. Fiber:
Fiber helps balance estrogen and progesterone levels and reduces the risk of ovulatory infertility. Oats, whole wheat bread, apples, pears, and beans are excellent options.
8. High-fat dairy:
Full-fat milk, yogurt, and cheese may reduce the risk of ovulatory infertility when consumed in moderation.
9. Iron-rich foods:
Low iron is associated with anovulation. Add lentils, spinach, pumpkin seeds, and fortified cereals to prevent deficiencies.
10. Choline:
Eggs, liver, salmon, and Brussels sprouts are good sources of choline, which supports ovarian function and protects against birth defects.
11. Superfoods for fertility:
Beetroot improves blood flow to the uterus, sweet potatoes support progesterone, ginger regulates periods, cinnamon helps with PCOS, tomatoes provide lycopene, and avocados deliver healthy fats and folate.
| Nutrient | Fertility Benefit | Best Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Folate | Healthy egg development, prevents defects | Spinach, kale, legumes, citrus |
| Omega-3 | Improves egg quality, hormone regulation | Salmon, chia seeds, walnuts |
| Vitamin D | Regulates hormones, supports ovulation | Egg yolks, salmon, fortified milk |
| Antioxidants | Protect eggs from oxidative stress | Berries, citrus, spinach |
| Iron | Prevents anovulation, supports ovulation | Lentils, spinach, pumpkin seeds |
| Choline | Supports ovarian function, reduces risk of birth defects | Eggs, salmon, legumes |
Have you ever wondered why two women of the same age may have different fertility outcomes? Diet often plays a bigger role than most people realize.
Foods to Avoid When Trying to Conceive:
Just as certain foods boost fertility, others can lower your chances of conception. Avoid or limit:
- Excess caffeine
- Alcohol
- Processed and junk foods
- High-mercury fish such as swordfish and king mackerel
- Trans fats and sugary drinks
- Refined carbs like white bread and soda
Also Read: What to Expect After Your IUI Treatment?
Sample Fertility Diet Plan:
Here’s a simple 1-day plan to show how you can incorporate fertility-friendly foods:
| Meal | Example Options |
|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal topped with berries, walnuts, and chia seeds |
| Mid-morning | Greek yogurt with pomegranate seeds |
| Lunch | Quinoa salad with spinach, avocado, chickpeas, and olive oil |
| Evening Snack | Carrot sticks with hummus |
| Dinner | Grilled salmon, roasted sweet potatoes, and steamed broccoli |
| Bedtime | Warm full-fat milk with a pinch of turmeric |
Isn’t it surprising that small food swaps, like choosing quinoa over white rice or salmon over red meat, can make such a big difference in fertility health?
Lifestyle Tips Along with Fertility Foods:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Engage in moderate exercise
- Reduce stress through meditation and yoga
- Prioritize 7–8 hours of sleep
- Stay hydrated with 2–3 liters of water daily
- Avoid environmental toxins like BPA and pesticides
Myths vs Facts About Fertility Foods:
When it comes to fertility, there are many food myths floating around. Let’s clear up the confusion with some simple facts:
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| Eating pineapple core helps with implantation | Pineapple is nutritious but won’t guarantee pregnancy. Balanced diet matters more. |
| Drinking lots of coffee reduces fertility | Moderate caffeine (1–2 cups/day) is usually safe. Excess may affect fertility. |
| Dairy products are bad for fertility | Full-fat dairy like milk, yogurt, and cheese in moderation can support fertility. |
| Only expensive superfoods boost fertility | Everyday foods like spinach, lentils, nuts, and eggs are equally effective. |
| Eating more protein always improves fertility | Too much animal protein may lower fertility. Focus on plant-based proteins like beans, quinoa, and chickpeas. |
| Going vegetarian guarantees better fertility | Plant-based diets are healthy, but a mix of plant and animal sources ensures complete nutrients. |
| Fertility foods work overnight | Diet helps over time. Consistency and a healthy lifestyle are more important than quick fixes. |
When to Consult a Doctor or Fertility Specialist:
Knowing when to seek professional help can save time and improve your chances of conception. Consider consulting a doctor or fertility specialist if:
- You have been trying to conceive for 12 months without success (or 6 months if you are over 35).
- You experience irregular menstrual cycles or missed periods.
- You have medical conditions such as PCOS, thyroid disorders, endometriosis, or other hormonal imbalances.
- You want personalized guidance on diet, supplements, or lifestyle changes to improve fertility.
- You have repeated miscarriages or difficulty maintaining a pregnancy.
- You suspect nutritional deficiencies like low iron, vitamin B12, or folate.
- You are planning to start fertility treatments like IVF or IUI and need expert monitoring.
- You want advice on ovulation tracking, fertility testing, or egg quality improvement.
- You are concerned about age-related fertility decline and want to explore options early.
Consulting a professional ensures that any underlying issues are identified and addressed, giving you the best chance for a healthy conception journey.
Conclusion:
Supporting female fertility naturally begins with understanding the strong link between nutrition, hormone balance, and reproductive health.
Did you know that research shows women who follow a fertility-focused diet have up to 50 percent higher chances of conceiving naturally compared to those with a poor diet? Choosing the right foods is a key step toward improving egg quality and overall reproductive health.
Incorporating nutrient-rich foods like leafy greens, nuts, whole grains, eggs, and fatty fish can provide essential vitamins, antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and iron. These nutrients support ovulation, regulate menstrual cycles, and reduce oxidative stress in reproductive cells.
Small dietary changes, like swapping refined carbs for complex carbohydrates or adding fiber-rich fruits and vegetables, can significantly enhance fertility outcomes.
Lifestyle factors also play a vital role alongside a fertility diet. Maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, getting adequate sleep, and engaging in moderate exercise can improve hormonal balance and optimize your body for conception. How often do you evaluate whether your daily meals and habits truly support your fertility goals?
Ultimately, consistent, mindful nutrition combined with a balanced lifestyle creates the best foundation for conception. By focusing on fertility-boosting foods today, you can increase your chances of a healthy pregnancy and prepare your body for motherhood naturally.
FAQs:
Leafy greens, nuts, seeds, eggs, whole grains, fatty fish, and fruits rich in antioxidants support fertility.
Yes, spices like turmeric, cinnamon, and ginger can reduce inflammation and support reproductive health.
Yes, eggs are rich in choline and protein, which improve egg quality and ovarian function.
Full-fat dairy like milk, yogurt, and paneer in moderation may help regulate hormones and support fertility.
Berries, oranges, pomegranates, guava, and papaya are rich in antioxidants and folate, supporting ovulation.
Yes, almonds, walnuts, pumpkin seeds, and flaxseeds provide omega-3s and vitamin E, supporting egg health.
Folate promotes healthy egg development and reduces the risk of neural tube defects in early pregnancy
Ayurvedic herbs like Ashwagandha and Shatavari may support hormonal balance and reproductive health.
Yes, high sugar, refined carbs, and junk food can cause inflammation and hormonal imbalance, reducing fertility.
Spinach, broccoli, carrots, sweet potatoes, and beetroot provide folate, beta-carotene, and antioxidants.
Moderate intake (1–2 cups/day) is generally safe, but excess caffeine may reduce conception chances
Yes, spinach, lentils, nuts, and fortified cereals help prevent anovulation caused by low iron.
Yes, male fertility also affects conception, so a balanced diet for both partners increases chances of pregnancy.