For individuals and couples starting the journey of intrauterine insemination (IUI), the period immediately following the procedure is often a combination of hope, anxiety, and anticipation.
This in-depth guide aims to make easy to understand the post-IUI experience, providing a day-by-day breakdown of what to expect, common symptoms, important considerations, and key facts to help you navigate this critical time with confidence.
Understanding the IUI timeline and implantation after IUI can significantly reduce stress during the two-week wait for a pregnancy test.
Understanding IUI: A Quick Overview
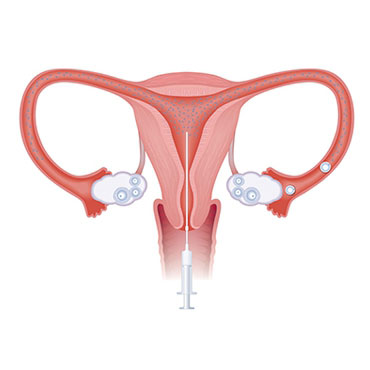
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a widely utilized fertility treatment and a type of artificial insemination. During this procedure, sperm that has been specifically washed and concentrated is directly placed inside your uterus during ovulation.
This strategic placement helps high-quality sperm get closer to the egg once it’s released by your ovaries, making it easier for the sperm to reach an egg by reducing the travel time and distance. This process ultimately aims to increase your chances of conception.
IUI is often considered before more invasive and costly fertility treatments like in vitro fertilization (IVF). People opt for IUI for various reasons, including certain infertility issues, as a reproductive option for same-sex female couples, or for single women desiring to conceive using donor sperm.
Conditions that may lead healthcare providers to recommend IUI include cervical mucus problems, low sperm count or other sperm impairments, ejaculation or erection dysfunction, semen allergy, or unexplained infertility.
The Immediate Aftermath: Days 1-2 Post-IUI
The IUI procedure itself is generally quick, lasting only a few minutes, comparable to a Pap test. A catheter is inserted through your cervix into your uterus to inject the prepared sperm sample.
What happens right after the procedure? Immediately after the insemination, your healthcare provider might ask you to lie down for about 10 to 30 minutes. This brief rest is primarily for your comfort in case you feel mild cramping or light-headedness, not to prevent sperm leakage, as the sperm is placed directly in the uterus.
During the first 1-2 days after IUI, it’s common to experience some mild symptoms:
- Mild cramping: This is a normal response as your body adjusts.
- Spotting: Light spotting for one or two days is also common and typically not a cause for concern. This could be cervical mucus dislodged during the procedure or a small amount of vaginal bleeding caused by the catheter.
Should you restrict your activities? While you can typically return to most normal activities right away, it’s often a good idea to take it easy.
Avoiding strenuous activities, such as high-intensity exercise, is generally recommended, especially if you’ve taken fertility medications that might leave your ovaries slightly enlarged and tender.
Swimming or bathing after IUI is also not advised to reduce the risk of infection. However, having sex after IUI is allowed and sometimes even encouraged, as uterine contractions from intercourse and orgasm can help sperm move towards the fallopian tubes. Some doctors may advise a short waiting period of up to 48 hours immediately after the procedure.
Must Read: How to Read a Semen Analysis Report
The Implantation Window: Days 3-9 Post-IUI
This period is crucial as it’s when implantation of a fertilized egg typically occurs. The IUI procedure is carefully timed to coincide with ovulation, often stimulated by fertility drugs and monitored with blood tests or ultrasounds.
After ovulation, the egg is viable for fertilization for only 12 to 24 hours. If fertilization occurs, the fertilized egg then needs to travel down the fallopian tube and implant in the lining of the uterus.
How long does implantation take after IUI? Implantation can take anywhere from 3 to 12 days after ovulation. Approximately 40% of women who become pregnant after ovulation experience implantation by the 9th day.
What are the signs of implantation after IUI? Implantation symptoms can be subtle and often mimic early menstruation or even side effects of the IUI procedure itself, making the “symptom guessing game” challenging. It’s important not to overanalyze every little detail.
Common signs of implantation include:
- Spotting: Known as “implantation bleeding,” this is usually very light, appearing as pink or light brown discharge rather than bright red blood. It occurs as uterine cells are dislodged when the blastocyst implants. It’s worth noting that spotting can also be a residual effect of the IUI catheter.
- Cramping: This is one of the most common implantation signs, though reported by only 30% to 35% of women who conceive. It might feel like slight twinges, a feeling of fullness in the abdomen, pinching, tingling below the navel, or mild gas pains. However, cramping can also signal impending menstruation or be a result of the IUI procedure itself.
During days 3-5, some women may also notice early signs like breast tenderness, bloating, or slight nausea due to hormonal changes, especially if taking progesterone supplements.
These symptoms are not definitive of pregnancy but are part of the early post-IUI experience. Around days 4-7, continued observation for these signs is recommended.
Monitoring Symptoms and Emotional Well-being: Days 10-14 Post-IUI
As you approach the end of the two-week wait, anticipation can intensify. Many of the physical symptoms you might experience, such as fatigue, mild cramping, or changes in appetite, can stem from both the IUI procedure and fertility medications.
What about emotional well-being during this time? The “two-week wait” is often described as an emotional rollercoaster, filled with hope, fear, and impatience.
It’s crucial to prioritize self-care and stress management during this period. Engaging in relaxing activities like meditation, yoga, journaling, reading, watching movies, or gentle walks can help manage stress and keep your mind occupied.
Leaning on your support system – partners, friends, family, or even fertility-specific support groups – is highly beneficial. If you feel disappointed or overwhelmed, talking with your healthcare provider or a counselor can provide valuable support.
The Pregnancy Test: When and How

When can you take a pregnancy test after IUI? Most healthcare providers advise waiting at least 14 days after the IUI procedure before taking a home pregnancy test.
This waiting period is critical because it takes time for human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), the pregnancy hormone, to build up to detectable levels in your blood or urine.
- False positives: Testing too early can lead to false positives, especially if you received an hCG “trigger shot” to stimulate ovulation, as the medication itself can be detected.
- False negatives: Conversely, testing too early can also result in false negatives if hCG levels haven’t yet risen enough to be detected, even if you are pregnant.
For the most accurate results from a home pregnancy test, follow the instructions carefully and use your first-morning urine, which typically has a higher concentration of hCG.
Your healthcare provider will often recommend a blood test at the clinic around two weeks after IUI for a definitive answer, as blood tests are more accurate.
Factors Influencing IUI Success:
The success rate of IUI is influenced by several factors, including the underlying cause of infertility, the use of fertility drugs, overall health conditions, and, most significantly, age.
IUI tends to work best for women with unexplained infertility, cervical mucus issues, or men with ejaculation problems. However, for conditions like fallopian tube disorders, endometriosis, or severe sperm impairment, IUI may not be as effective, and treatments like IVF might be more suitable.
Age plays a crucial role in IUI success, as egg quality and quantity naturally decline with age. Healthcare providers generally recommend IUI before age 40 to maximize the chances of success.
Here’s a breakdown of the IUI pregnancy rate by age:
| Age Group | IUI Pregnancy Rate |
| 20 to 30 | 17.6% |
| 31 to 35 | 13.3% |
| 36 to 38 | 13.4% |
| 39 to 40 | 10.6% |
| Over 40 | 5.4% |
When fertility drugs are used, the pregnancy rate for IUI can be as high as 20%, bringing the success rate closer to that of natural conception.
Most healthcare providers suggest trying three cycles of IUI before considering other reproductive treatments like IVF, though for women over 40, some might recommend just one cycle before moving to IVF due to higher success rates with IVF in that age group and the importance of timely treatment.
Risks and Side Effects of IUI:

IUI is considered a low-risk procedure compared to more invasive fertility treatments like IVF. However, some potential risks and side effects exist:
- Multiple births: If fertility medication is used to stimulate your ovaries, you might release more than one egg, increasing the chance of conceiving twins, triplets, or more. Multiple pregnancies carry higher risks such as premature labor and low birth weight.
- Infection: This is a rare complication.
- Spotting: Mild vaginal bleeding can occur due to the procedure.
- Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS): A rare side effect caused by taking too much fertility medication, leading to painful and swollen ovaries.
Common mild side effects, especially from fertility medications, include cramping and spotting after insemination.
IUI vs. IVF: Understanding Your Options
Is IUI better than IVF? Neither treatment is inherently “better” than the other; rather, one may offer a higher chance of conceiving based on individual circumstances. Most people initially try IUI because it is generally more affordable and less invasive than IVF.
What’s the difference? With IUI, fertilization occurs inside your fallopian tube. Sperm are prepared and inserted into your uterus to help them reach the egg more easily.
In contrast, with IVF, sperm and eggs are fertilized outside your body in a lab, and the resulting embryo is then placed into your uterus. IVF typically has a higher success rate per cycle but is more expensive and invasive. Your healthcare provider will help determine which treatment is best suited for your specific needs.
Lifestyle Recommendations Post-IUI:

Beyond the medical procedures, your lifestyle choices can support your overall well-being during this time:
- Activity: Light to moderate exercise like walking or yoga is generally safe, but avoid high-impact activities. Listen to your body and avoid overexertion.
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, including whole foods, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, is recommended. Taking folic acid (often in prenatal vitamins) is advised at least three months before conception or IUI treatment.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water.
- Avoid certain substances: Refrain from smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and reduce caffeine intake to improve your chances of pregnancy success.
- Stress Management: Practice mindfulness, meditation, or counseling to manage stress, which can positively impact your body’s ability to support a pregnancy.
When to Contact Your Healthcare Provider
While mild symptoms are common, certain signs warrant immediate medical attention. You should contact your healthcare provider if you experience any of the following, especially if you’re taking fertility medications:
- Severe pelvic or abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Shortness of breath
- Sudden weight gain
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Heavy, bright red bleeding
These symptoms could indicate complications such as ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) or infection.
Conclusion:
The journey after IUI is a unique and often challenging experience, spanning from immediate physical sensations to the emotional intensity of the two-week wait for a pregnancy test.
By understanding the IUI process day-by-day, monitoring symptoms, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and leaning on a strong support system, you can navigate this period with greater peace of mind. Remember, your healthcare provider is your best resource for personalized guidance and support throughout your fertility treatment journey, helping you determine the best path to achieve a successful pregnancy.
FAQs:
The procedure bypasses the cervix by placing prepared sperm directly into your uterus with a catheter, significantly reducing the distance it has to travel to reach your fallopian tubes and the egg. This makes it easier for sperm to reach an egg, thereby increasing your chance of becoming pregnant.
People choose IUI for various reasons, including infertility issues, as a reproductive option for same-sex female couples, or for females wishing to conceive without a partner using donor sperm. Healthcare providers often try IUI before other more invasive and expensive fertility treatments.
IUI may be used for cervical mucus problems, low sperm count or other sperm impairments, when using donor sperm, or for ejaculation/erection dysfunction. It can also be effective for a semen allergy (as proteins are removed) or for unexplained infertility.
In IUI, fertilization occurs inside your fallopian tube, similar to natural conception, after a washed sperm sample is inserted into your uterus. With IVF, the sperm and egg are fertilized outside your body in a lab, and then the resulting embryo is placed into your uterus.
The entire IUI process, from beginning to end, is approximately four weeks (around 28 days), which is about the same length as a regular menstrual cycle. The insemination procedure itself is very quick, taking just a few minutes.
Yes, it is common to experience mild cramping and spotting for one or two days after IUI. You may also have vaginal discharge, which is normal and not “leakage” of sperm,
Yes, you can have sex before and after IUI; some healthcare providers even encourage intercourse and orgasm after the procedure. Uterine contractions caused by orgasm can potentially help push sperm towards the fallopian tubes and the egg.
Common implantation signs include spotting (usually pink or light brown and minimal blood, unlike a period) and cramping (slight twinges or a feeling of fullness below the navel). These symptoms can be subtle and often mimic early menstruation or side effects of the IUI procedure itself.
IUI can be highly effective, especially when fertility drugs are used, with pregnancy rates potentially as high as 20%. It helps bring people’s chances up to a more typical success rate, similar to natural conception (around 20%).
Most healthcare providers recommend three cycles of IUI before pursuing another reproductive treatment like IVF. However, if you are over 40 or have conditions like endometriosis or fallopian tube damage, some may recommend fewer IUI cycles or going directly to IVF.
IUI is considered low risk compared to IVF, but risks include multiple births (if fertility medication is used), rare infection, spotting, and very rare ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). Mild cramping and spotting are common after the insemination procedure.
IUI is often combined with fertility medications to stimulate the ovaries, though not always necessary; common ones include Clomiphene citrate, Letrozole, hCG (as a trigger shot), and FSH. Taking prenatal vitamins (which include folic acid) is also recommended for all pregnancies.
You should contact your healthcare provider immediately if you experience severe pelvic or abdominal pain, heavy bright red bleeding, nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, sudden weight gain, dizziness, or lightheadedness. These could be signs of complications like infection or other very rare side effects.

[…] Must Read: What to Expect After Your IUI Treatment? […]
[…] Must Read: What to Expect After Your IUI Treatment […]
[…] Also Read: What to Expect After Your IUI Treatment […]
[…] Also Read: What to Expect After Your IUI Treatment […]
[…] Also Read: What to Expect After Your IUI Treatment […]
[…] IUI (Intrauterine Insemination) – Washed sperm placed directly in uterus. […]
[…] Also Read: What to Expect After Your IUI Treatment? […]
[…] Also Read: What to Expect After Your IUI Treatment […]