Infertility is no longer a rare issue in India or globally – it’s a growing health concern. One real example is from Mumbai, where a young couple in their late 20s had been trying to conceive for over three years. The woman’s fertility reports were normal, but the man’s semen analysis revealed low sperm count and poor motility. With timely intervention, including hormonal therapy and assisted reproductive technology (ART), the couple finally conceived.
This case proves an important fact: infertility is not just a “woman’s problem.” Studies show that male factors contribute to 20–30% of infertility cases worldwide. Yet, stigma, lack of awareness, and delayed medical consultation often worsen the issue.
This comprehensive guide explores male infertility causes, symptoms, types, diagnosis, treatments, costs, myths, and prevention tips – backed by medical facts and the Indian context.
What is Male Infertility?

Male infertility is the inability of a man to cause pregnancy in a fertile woman after at least 12 months of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse.
It mainly occurs due to problems in sperm production, sperm quality, or sperm delivery. Even if sperm are produced in adequate numbers, abnormalities in motility or morphology can still prevent fertilization.
Common medical terms in male infertility:
- Oligospermia – Low sperm count.
- Azoospermia – No sperm in semen.
- Asthenozoospermia – Poor sperm motility.
- Teratozoospermia – Abnormal sperm shape.
- Hypogonadism – Low testosterone affecting sperm production.
Prevalence of Male Infertility in India
Infertility is rising due to lifestyle changes, stress, and environmental pollution. In India, about 15% of couples face infertility, and nearly half of these cases are due to male factors.
| Factor | Percentage Contribution |
|---|---|
| Male Infertility | 40–50% |
| Female Infertility | 30–40% |
| Combined Factors | 10–15% |
| Unexplained Infertility | 10% |
This shows why male reproductive health is equally important in fertility discussions.
Causes of Male Infertility:

Male infertility can be caused by low sperm count, poor sperm motility, or abnormal sperm shape. Other factors like hormonal issues, lifestyle habits, and medical conditions also play a major role.
1. Medical Causes:
- Varicocele – Enlarged veins in the scrotum, reducing sperm quality.
- Infections – STDs, mumps orchitis, prostatitis, tuberculosis.
- Hormonal Imbalances – Low testosterone, abnormal FSH/LH, thyroid issues.
- Genetic Disorders – Klinefelter syndrome, Y-chromosome microdeletions.
- Testicular Problems – Undescended testes, injury, trauma.
- Ejaculation Disorders – Retrograde ejaculation, premature ejaculation.
- Tumors – Testicular or pituitary tumors interfering with hormones.
2. Lifestyle and Environmental Causes:
- Excessive smoking, alcohol, and recreational drugs.
- Obesity and lack of physical activity.
- High stress, depression, and poor sleep cycles.
- Heat exposure (hot tubs, laptops on lap, tight underwear).
- Exposure to pesticides, radiation, or heavy metals.
3. Age-Related Causes:
Men above 40 show decreased sperm motility, morphology, and DNA integrity, reducing fertility chances.
Also Read: Top 10 IVF Centers in Mumbai
Symptoms of Male Infertility:

Male infertility may not always show obvious symptoms apart from difficulty in conceiving. Still, warning signs may include:
- Low sperm count and abnormal semen analysis.
- Difficulty in erection or ejaculation.
- Low sex drive.
- Swelling or pain in testicles.
- Reduced facial or body hair.
- Enlarged male breasts (gynecomastia).
Types of Male Infertility:
- Pre-testicular Infertility – Hormonal imbalances or problems with the pituitary gland.
- Testicular Infertility – Damage to testicles due to infection, trauma, or varicocele.
- Post-testicular Infertility – Issues with sperm transport due to blockages or ejaculation disorders.
How is Male Infertility Diagnosed?
Diagnosis requires a combination of physical examination, lab tests, and imaging.
Common Diagnostic Tests:
- Semen Analysis – Checks sperm count, motility, morphology, and volume.
- Hormonal Tests – Testosterone, FSH, LH, prolactin, thyroid hormones.
- Genetic Testing – For chromosomal abnormalities or Y-chromosome defects.
- Ultrasound of Scrotum – Detects varicocele or obstructions.
- Post-ejaculation Urinalysis – For retrograde ejaculation cases.
Common Question: “If my sperm count is normal, can I still be infertile?”
Yes. Even with normal sperm count, poor motility, abnormal morphology, or DNA fragmentation may still cause infertility.
Treatment Options for Male Infertility:
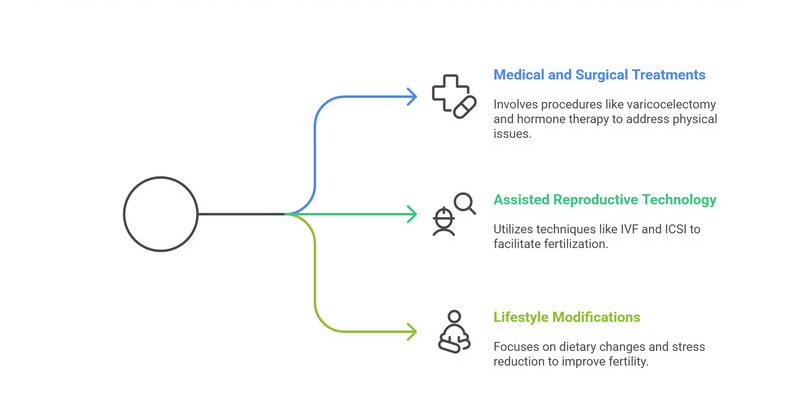
Male infertility can be treated through lifestyle changes, medications, hormone therapy, or assisted reproductive techniques like IVF and ICSI.
1. Medical and Surgical Treatments:
- Varicocelectomy – Surgery to repair varicocele.
- Hormone Therapy – Testosterone replacement or FSH/LH therapy.
- Medications – Antibiotics for infections.
- Surgery for Blockages – Corrects obstruction in sperm transport.
2. Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART):
- IUI (Intrauterine Insemination) – Washed sperm placed directly in uterus.
- IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) – Eggs and sperm fertilized in lab.
- ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) – A single sperm injected into an egg.
- Sperm Retrieval – TESE, PESA, MESA for azoospermia cases.
3. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Eating a balanced diet with zinc, selenium, omega-3, and antioxidants.
- Maintaining healthy weight.
- Quitting smoking, alcohol, and drugs.
- Reducing stress with meditation and yoga.
- Avoiding prolonged heat exposure to testicles.
Must Read: How Many Injections Are Needed for IVF Treatment?
Diet and Supplements for Male Fertility:
Certain foods and supplements boost sperm quality:
- Zinc-rich foods – Pumpkin seeds, lentils, chickpeas.
- Antioxidants – Vitamin C, Vitamin E, CoQ10.
- Omega-3 fatty acids – Fish, walnuts, flaxseeds.
- Folic Acid – Supports sperm DNA quality.
- L-carnitine – Improves sperm motility.
Cost of Male Infertility Treatment in India:
Costs can vary depending on the cause and treatment type:
| Treatment/Test | Approx. Cost (INR) |
|---|---|
| Semen Analysis | 500 – 1,500 |
| Hormonal Tests (FSH, LH, T) | 1,500 – 4,000 |
| Varicocele Surgery | 50,000 – 80,000 |
| IUI Procedure | 10,000 – 20,000 |
| IVF Treatment | 1.5 – 2.5 Lakhs |
| ICSI Procedure | 2.0 – 3.0 Lakhs |
Best Practices to Choose a Male Infertility Specialist in India:
- Look for andrologists or urologists with fertility expertise.
- Check success rates of ART procedures at the clinic.
- Ensure lab facilities have advanced semen analysis and genetic testing.
- Seek centers accredited by ICMR or reputed medical associations.
Male Infertility & Sexual Health Connection:
Sexual health issues often overlap with infertility:
- Erectile Dysfunction – Can prevent intercourse.
- Low Libido – Due to low testosterone or stress.
- Premature Ejaculation – Impacts successful conception.
Treatment may involve hormone therapy, counseling, or medications alongside fertility treatment.
Also Read: Top 10 IVF Centers in Delhi
Male Infertility Myths vs. Facts:
Male infertility is often surrounded by myths, but the truth is rooted in science and lifestyle factors. Let’s clear the confusion with real facts that break the common misconceptions.
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| Infertility is only a woman’s issue. | Male factors cause ~50% of cases. |
| A man with normal sperm count is fertile. | Quality (motility, DNA) matters too. |
| Age doesn’t affect male fertility. | Fertility declines after 40. |
| Only unhealthy men are infertile. | Even fit men can face genetic or hormonal issues. |
| Infertility means no chance of fatherhood. | With ART, many men become fathers. |
Emerging Treatments & Research in Male Infertility:
- Stem Cell Therapy – Still experimental, potential to restore sperm production.
- Advanced Sperm Selection (IMSI, MACS) – Picks healthier sperm for IVF/ICSI.
- Gene Editing Research – Future solution for genetic infertility causes.
Psychological and Social Impact:
Male infertility can cause stress, low self-esteem, depression, and marital conflicts. Counseling, support groups, and open communication between partners are vital for emotional well-being.
Checklist: When Should a Man Visit a Fertility Doctor?
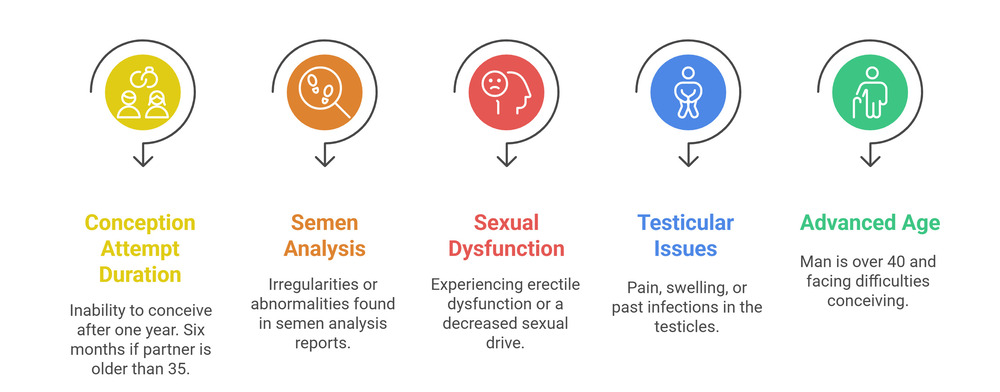
- Tried conceiving for 12+ months (or 6 months if partner >35).
- Abnormal semen analysis reports.
- Erectile dysfunction or low libido.
- Testicular pain, swelling, or history of infections.
- Age above 40 with conception difficulties.
Conclusion:
Male infertility is a growing concern worldwide, including India. It is responsible for nearly half of infertility cases among couples. The good news is that with early diagnosis, proper treatment, ART options, and lifestyle modifications, most men can overcome infertility and achieve parenthood.
If you or your partner suspect infertility, don’t delay – consult a fertility specialist. Remember, infertility is a medical condition, not a personal failure. With the right treatment and awareness, parenthood is very much achievable.
FAQs:
Yes. Chronic stress alters hormones like cortisol and testosterone, reducing sperm production.
WHO defines normal sperm count as 15 million sperm per ml or more.
If a couple under 35 fails to conceive after 12 months, or over 35 after 6 months, medical evaluation is advised.
Mild cases caused by lifestyle factors can improve with diet, exercise, and quitting smoking/alcohol. Severe cases require medical treatment
Yes. Fertility decreases after 40, with higher chances of DNA damage in sperm
It is a condition where no sperm is present in semen. Treatment includes sperm retrieval, ICSI, or donor sperm.
Not always. Treatments like hormone therapy, varicocele repair, and IUI may work depending on the cause.
Yes, regular marijuana use can lower sperm count and reduce sperm motility, which may contribute to male infertility. However, the effect can vary based on frequency and lifestyle factors.
The usual dosage of clomiphene citrate for men ranges between 25–50 mg daily, but it should only be taken under medical supervision. Dosage depends on hormonal test results.
Not always. Many causes of male infertility are treatable with medications, surgery, or assisted reproductive techniques like IVF or ICSI.
The four common causes are low sperm count, poor sperm motility, hormonal imbalances, and structural issues like varicocele.
Yes, depending on the cause. Treatments include medications, surgery, lifestyle changes, or advanced fertility techniques that can help couples conceive.
Clomid (clomiphene citrate) is often prescribed to boost testosterone and sperm production in men with hormonal imbalances. It is effective for some but not all cases.
Ayurveda suggests natural remedies like Ashwagandha, Shilajit, and Safed Musli to improve sperm quality and vitality, but scientific evidence is limited.
Low sperm count (oligospermia) is the most common type of male infertility, often linked with lifestyle factors or medical conditions.
Yes, type 2 diabetes can affect sperm quality, erectile function, and hormone levels, increasing the risk of male infertility.

[…] Male infertility: Low sperm count, poor sperm motility, abnormal sperm shape, or issues requiring sperm retrieval. […]
[…] treatment is often recommended for couples facing unexplained infertility, low sperm motility, mild male factor infertility, or ovulation […]
[…] male infertility, female infertility, and unexplained […]
[…] couples navigating male infertility or issues like low sperm count diagnosed via semen analysis, this added setback can feel […]